The Endocannabinoid System: Your Body's Master Regulator
Have you ever wondered how CBD or other cannabinoids actually work in your body? The answer lies in a powerful and complex biological network that most people have never heard of: the Endocannabinoid System, or ECS.
A recent review in the journal Biological Psychiatry called the ECS a "widespread neuromodulatory network" that plays a major role in "tuning many cognitive and physiological processes." In simpler terms, the ECS is your body's internal balancing system, constantly working behind the scenes to keep everything in harmony.
What Exactly Is the ECS?
Think of your body as a high-performance orchestra. The ECS is the conductor, ensuring every section—from your sleep patterns and mood to your pain responses and immune function—is playing at the right volume and tempo. When a section is out of tune, the ECS steps in to bring it back into balance, a state known as homeostasis.
The ECS is made up of three core components:
-
Endocannabinoids: These are the "messengers." Your body naturally produces these small molecules on demand to send signals throughout the nervous system. The two most studied endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-AG.
-
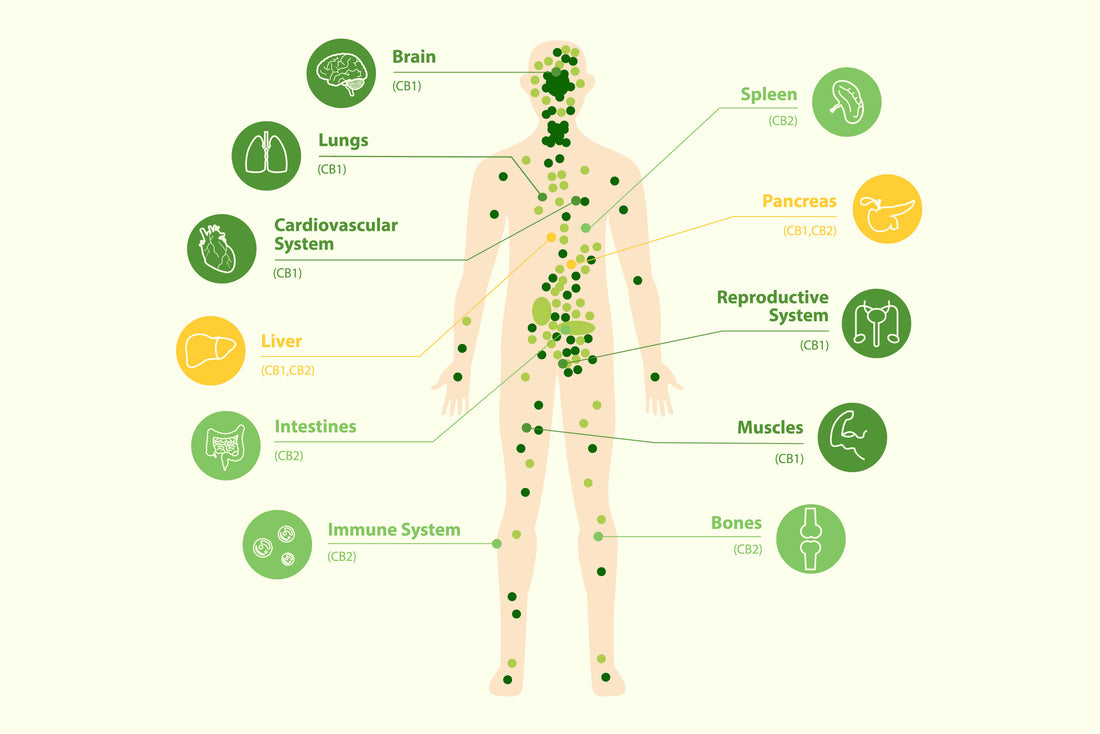
Cannabinoid Receptors: These are the "receivers" or "locks" on the surface of your cells. The two primary receptors are CB1 (found mostly in the central nervous system, influencing things like mood and memory) and CB2 (found mostly in the immune system and peripheral tissues, influencing inflammation and pain).
-
Enzymes: These are the "cleanup crew." Once an endocannabinoid has delivered its message and done its job, enzymes quickly break it down, ensuring the system is always responsive and ready for the next signal.
How Plant-Based Cannabinoids Interact with Your ECS
This is where compounds from the cannabis plant, known as phytocannabinoids (like CBD), come into the picture. They don't just introduce something foreign into your body; they interact with your pre-existing ECS.
While THC causes a "high" by binding directly to the CB1 receptors in your brain, CBD works differently. It doesn't directly bind to the receptors. Instead, it's believed to influence the ECS by:
-
Slowing the "Cleanup Crew": CBD can inhibit the enzymes that break down your body’s natural endocannabinoids. This allows your own internal messengers to stay active for longer, helping the ECS work more effectively.
-
Influencing Other Receptors: CBD also interacts with other non-cannabinoid receptors, such as those that regulate pain perception and anxiety, to produce its calming effects.
The Path Forward
This scientific review and others like it are a crucial part of the conversation happening around the world. They highlight that the ECS is a vital system for maintaining wellness, and that plant-based cannabinoids are gaining attention because of their ability to support this natural network.
Understanding how your body's own systems work is the first step toward making informed decisions about your health. As research into the ECS continues to grow, we are confident that a deeper understanding will empower people to find the best ways to achieve balance and well-being.
As always, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health, especially if you are considering adding new products to your wellness routine.